The mechanism of Originator Profile
VCs that configure Originator Profile
As mentioned in What is an Originator Profile?, Originator Profile (OP) and Content Attestation (CA) use a data model based on Verifiable Credentials (VCs).
The VCs handled by Originator Profile are defined in the following table.
| Name | Purpose | Content | Issuer | Distribution format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Profile (CP) | Guaranteeing the authenticity of OP holder organization | Public key of OP holder organization | OP Registry (OP Issuer) | Originator Profile Set (OPS) |
| Web Media Profile (WMP) | Display of OP holding organization information for web users | Web media name, etc | OP Registry (OP Issuer) | Originator Profile Set (OPS) |
| Profile Annotation (PA) | Additional information for OP holder organization | OP holder's organizational existence, industry association affiliation, certifications, etc | The organization that determines the eligibility of the sender (PA issuer) | Originator Profile Set (OPS) |
| Website Profile (WSP) | Representation that the website is operated by the OP holding organization | Website name, etc | Sender | Site Profile (SP) |
| Content Attestation (CA) | Guaranteeing the authenticity of Web content | Hashes of content data, etc | Sender | Content Attestation Set (CAS) |
These VCs are digitally signed by the issuer, so it is possible to confirm that the contents have not been tampered with. Another advantage of the IHV model is that when web users verify these VCs, they do not need to access the web server for verification, which eliminates privacy concerns.
Although the table does not list a VC called Originator Profile (OP), OP is not a single VC, but a data format consisting of CP, WMP, and PA. This allows for flexibility, such as issuing by the appropriate issuer on a VC-by-VC basis and replacing VC depending on the use case.
Relationship diagram
The following diagram shows the relationship between the issuers of VCs that make up the Originator Profile and the interactions that take place between them and Web users.
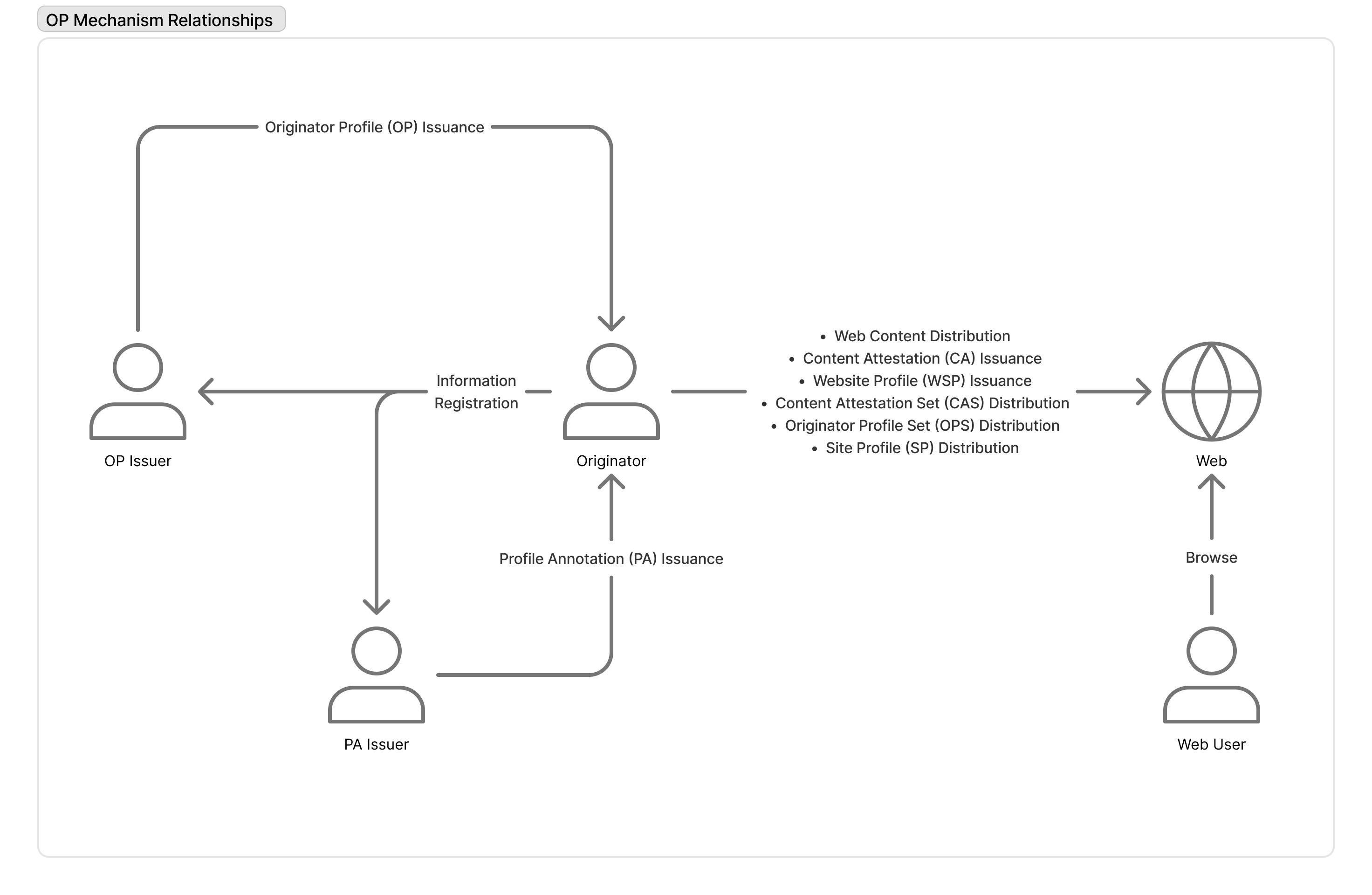
The originator provides the OP Issuer and PA Issuer with the information required to issue VCs, which then issue the OP and PA, respectively.
After receiving OP and PA, the originator issues CAs and WSPs based on the web content it originates, and stores the respective VCs in the appropriate distribution formats of CAS, OPS, and SP, and distributes them to the web along with the web content.
Web users can obtain VCs when browsing the web and verify the authenticity and reliability of the sender and content.
Web use
In order for an originator to distribute the VCs handled by their Originator Profile along with their web content on the web, they must follow the HTML linking of OPS and CAS , and the format of SP. This allows web users to view the VCs associated with web content using a browser extension specifically for OP.
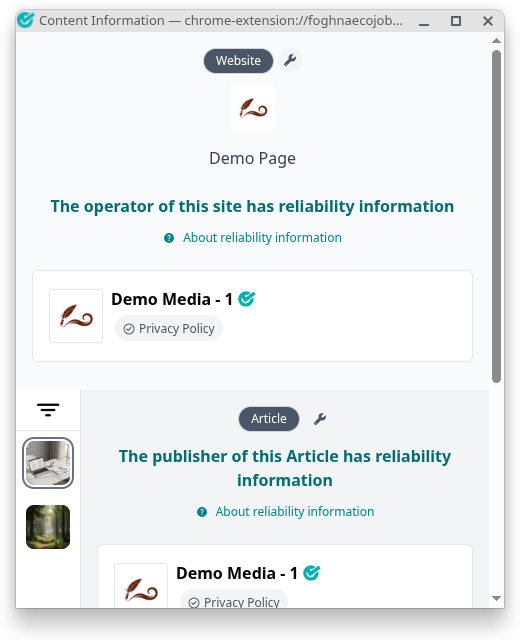
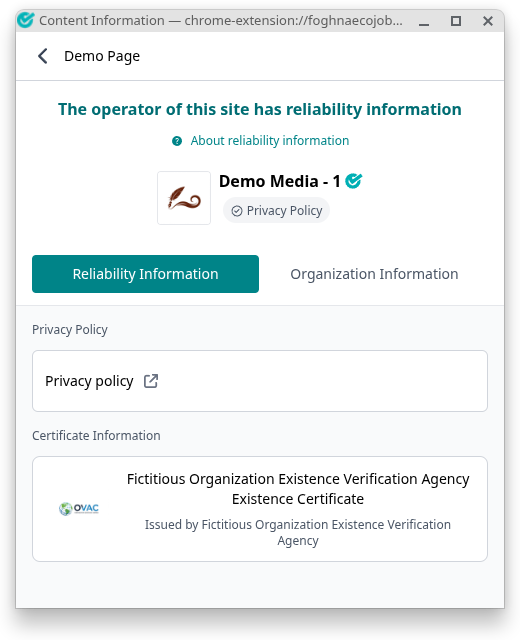
The location of each piece of web content within the page is also identified.
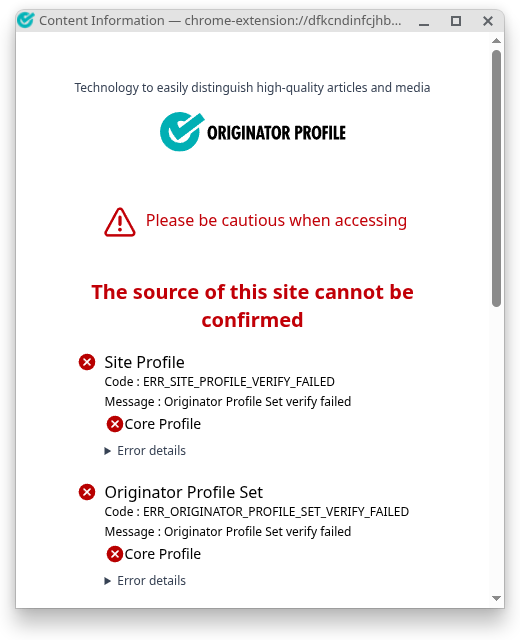
If VCs fail to validate, the extension will display a verification failed screen, warning the user that they may be browsing an unsafe site.